Bits & Binary
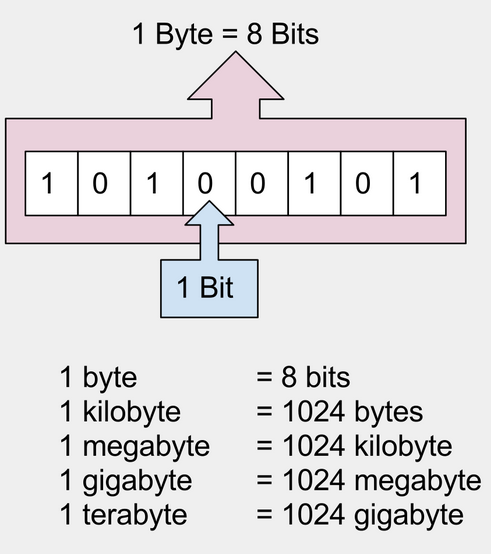
Binary is a number system (base 2 ) and bit is the basic unit for information storage.
Any number system has digits based on the base. Binary being a base 2 number system has two types of digits 0 and 1. Each of these take 1 bit of storage.
An octet is 8 binary(0,1) digits or 8 bits. Ex:10100110.

1 = There is signal = High voltage
0 = There is no signal = Low voltage
Chart= 128 to 1 , 27 to 20

If numbers are turned on from right to left the sum will always be equal to left number -1.
Essentially there are four things that have to exist for a network to be a network.
- A network address
- A host on the network
- A broadcast address
- A subnet mask
In any IP address there are two parts that is Network Part and Host part, the network Part is used to Identify Network and Host part used to specify number of supported hosts.
A network ID given to an address, identifies which network you’re on and a host ID is the address of the devices on the network.
(ID means IP address)
Network ID identifies which network you are on so when you receive traffic your devices know that it comes from the same network it’s directly connected to or if it needs to reply to a network that it doesn’t currently have knowledge of.
Broadcast address is used to speak to every device on the network at the same time.
It is a special IP address used to transmit messages and data packets to network systems. Network administrators verify successful data packet transmission via broadcast addresses.
- Broadcast IP address is used to indicate that packets being sent out should be delivered to every single client on the LAN. These addresses are always the highest number possible in a network address or subnet.
- Routing protocols such as Routing Information Protocol (RIP) use broadcasts to send out “ads”. This advertisement is used by routers to map the topology of a network, so that the data can be routed to the required place.(This protocol will attempt to find the fasted route through a network to a destination, based on how many “hops” it takes to get from the sender to the receiver.)
- Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) uses broadcast IPs to map physical addresses to logical addresses. A device sends a broadcast to every other device on the network to essentially find out who is where.
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) uses broadcasts to dynamically assign an IP address to computers on a network.
Networks used to have classes like A, B, C and these classes could help identify networks, however due to the need to create different sized network CIDR or slash notation was created to cope with this problem and identify the size of the network or subnet.
Classes
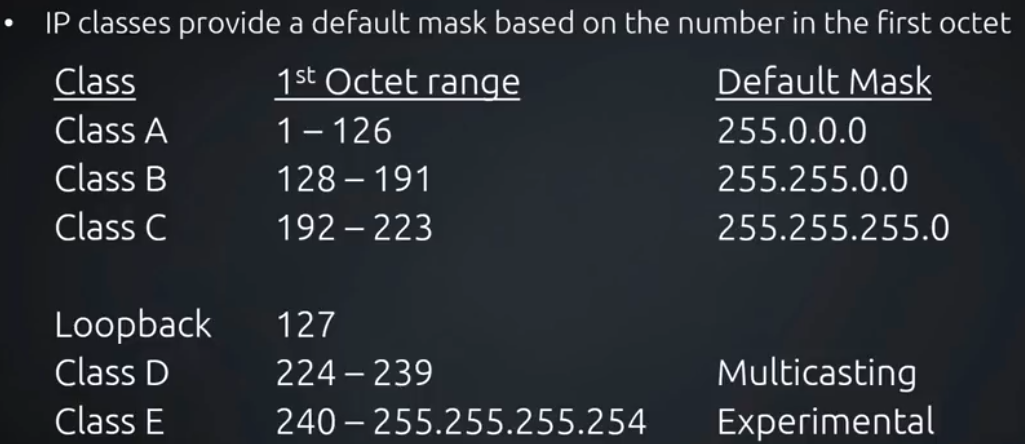
Lets take an Example : 192.168.1.1 and 192.168.2.1
Here the given Class C IP address changes at the third Octet hence differentiates the network 192.168.1.x and 192.168.2.x the .1 and .2 shows they are different networks.
Again taking the Class C IP address as an example , the ‘X’ in 192.168.1.X, is the Host part, the IPs assigned to Network Devices , it varies from 1 to 254 , assigned to host machines.
- In a class A address, the first octet is the network portion,so in this IP 10.1.25.1, first octet portion (10) is the network part and rest (1.25.1) are the host portion (the next 24 bits).
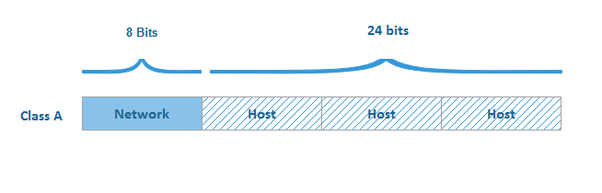
- In a class B address, the first two octets are the network portion, ie 172.16. of IP 172.16.126.220, and rest (the next 16 bits) are for the hosts.
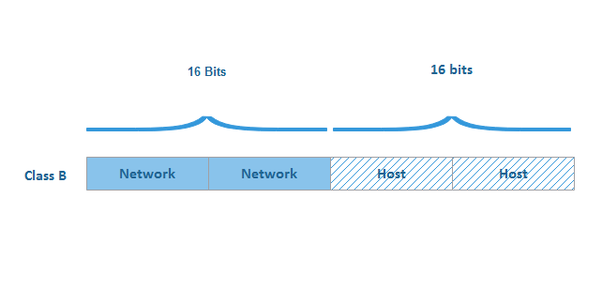
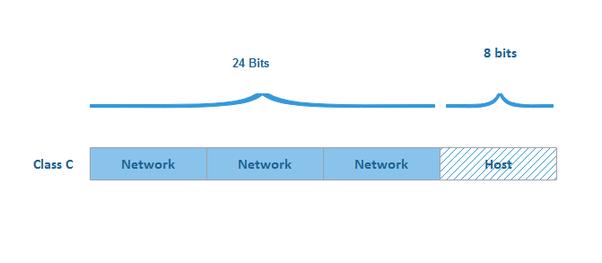
- In a class C address, the first three octets is the network portion,so in this IP 192.168.45.55, first 3 octets portion (192.168.45) are the network part and rest (55) is the host portion (the next 8 bits).
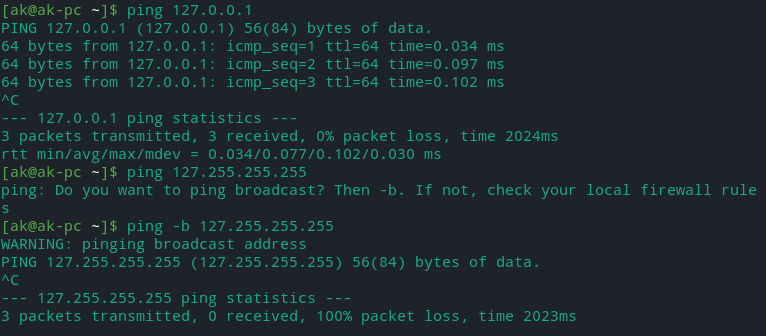
- Loopback means basically we are pinging are ourselves any address that start with 127 is a loopback.
First address = 127.0.0.1 (localhost) - We can not ping 127.255.255.255 because it is the broadcast address.Pinging broadcast address will ping all the hosts in the network and not all devices will reply beacuse it is disabled in some devices as a security feature because one could spoof the origin to flood any host on the network.
-
Multicasting is similar to broadcasting, but only transmits information to specific users. It is used to efficiently transmit streaming media and other types of data to multiple users at one time.
-
Class E address are never used because they are for experimental research.
- Broadcast address for all networks - 255.255.255.255
CIDR
Classless InternDomain Routing
(CIDR, pronounced like “cider”) notation is a compact way to represent an IP address along with its associated subnet mask and routing prefix.
CIDR notation = 192.168.100.0/24
/24 tells the number of binary digits turned on in our subnet masks.
In this case first 24 bits are turned on.
The /24 tells you that the first 24 bits of the IP address are used for network routing, and also that of the subnet mask contains 24 binary bits set to 1 (255.255.255.0), which also holds true for each IP address on the same subnet.
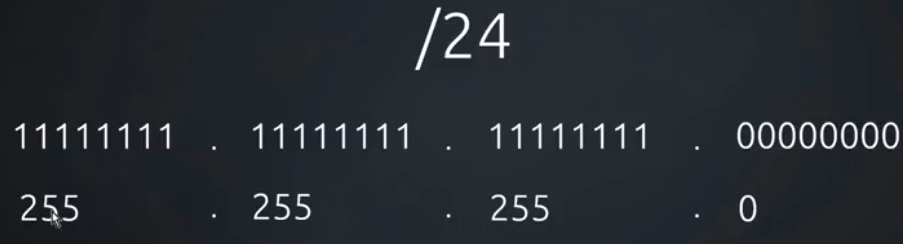
/24=8+8+8+0 (since in 255.255.255.0 there are 3 completely turned on octets)
To calculate any subnet mask add left to right (choose highest number first).
-
Mask tells us to use only those bits in the ‘network id’ which are part of the masks(numbers turned on in the 128 to 1 chart).
-
A subnet mask identifies how many addresses(host) you can have on your network.
Since an IPv4 address contains 32 bits, this means that the remaining 8 bits are used for calculating host IDs in /24.
In the above example you can have 256 address as zero is a number. -
Note there are two fewer hosts than available addresses because two addresses are always reserved for the network and broadcast IDs.
If the first three octets of the subnet mask are 255.255.255.x then the Network ID will always contain 192.168.y.y